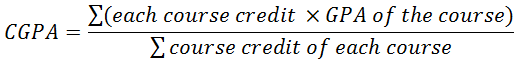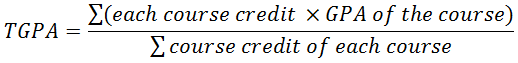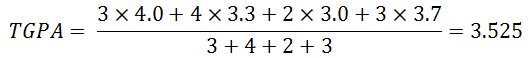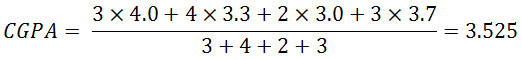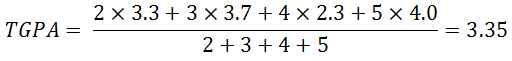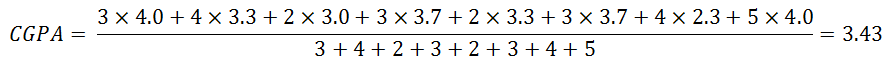Understanding GPA Calculation For Bachelor In University (Montreal City)
Introduction of GPA
GPA stands for Grade Point Average. It’s a measurement for the employers or schools to compare which students performed better academically. However, the GPA calculation is a little bit different in different university. So GPA is one of the tools to compare students, although this is not the only criteria that employers or schools look at. For example, another criterion will be the ranking of the university. The better university ranks, meaning the better the students learns which leads to a better future career. Let’s focus on how we calculate GPA in the great Montreal City.
Rating scale from letter grade to GPA
| GPA Table | A+/A* | A | A- | B+ | B | B- | C+ | C | C- | D+ | D | D- | E | F |
| McGill | NA | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | NA | NA | 1.0 | NA | NA | 0.0 |
| Concordia | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.7 | NA | 0.0 |
| H.E.C. | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | NA | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Polytechnique | 4.0 | 4.0 | NA | 3.5 | 3.0 | NA | 2.5 | 2.0 | NA | 1.5 | 1.0 | NA | NA | 0.0 |
| Montréal | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | NA | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| U.Q.A.M. | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | NA | 0.0 | NA |
| É.T.S. | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | NA | 0.0 | NA |
| Sherbrooke | 4.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | NA | 0.0 | NA |
| Laval | 4.33 | 4.00 | 3.67 | 3.33 | 3.00 | 2.67 | 2.33 | 2.00 | 1.67 | 1.33 | 1.00 | NA | 0.00 | NA |
*NA means the university does not use this grade.
Any other letter will have a GPA of 0, unless the course is dropped before the course drop deadline.
Calculation of CGPA and TGPA
TGPA is the average GPA of the term and CGPA is the average GPA of all the courses taken in university. However they are calculated the same way. The only different is the number of courses. We use the following equations:
For example
A student is from McGill University, based on the GPA Table, the GPA for each course is converted in the table below.
First term of university
|
Course Name |
Units/credits Obtained |
Grade Obtained |
GPA of the course |
|
Math 101 |
3 |
A |
4.0 |
|
English 202 |
4 |
B+ |
3.3 |
|
Comp 104 |
2 |
B |
3.0 |
|
Bio 105 |
3 |
A- |
3.7 |
Second term of university
|
Course Name |
Units/credits Obtained |
Grade Obtained |
GPA of the course |
|
Math 204 |
2 |
B+ |
3.3 |
|
Chem 201 |
3 |
A- |
3.7 |
|
Comp 205 |
4 |
C+ |
2.3 |
|
Bio 303 |
5 |
A |
4.0 |
The cumulative GPA is combining the first term and second term’s GPA.
Rating scale from numerical percentage grade to letter grade
The table below is a general converting system for the university. The professors have the final decision on the grading system. They can change the conversion base on the average of the class, or the understanding of the students. Also, different department (program) can give different conversion.
|
% Grade Table |
University of McGill |
University of Concordia |
H.E.C. |
Université de Montréal |
|
A+/A* |
NA |
90-100 |
90-100 |
90-100 |
|
A |
85-100 |
85-89 |
85-89 |
85-89 |
|
A- |
80-84 |
80-84 |
80-84 |
80-84 |
|
B+ |
75-79 |
77-79 |
77-79 |
77-79 |
|
B |
70-74 |
73-76 |
73-76 |
73-76 |
|
B- |
65-69 |
70-72 |
70-72 |
70-72 |
|
C+ |
60-64 |
67-69 |
67-69 |
65-69 |
|
C |
55-59 |
63-66 |
63-66 |
60-64 |
|
C- |
NA |
60-62 |
60-62 |
57-59 |
|
D+ |
NA |
57-59 |
57-59 |
54-56 |
|
D |
50-54 |
53-56 |
53-56 |
50-53 |
|
D- |
NA |
50-52 |
NA |
NA |
|
E |
NA |
NA |
35-52 |
35-49 |
|
F |
0-49 |
0-49 |
0-34 |
0-34 |
*NA means the university does not use this grade.
- ETS de Montréal and Polytechnique de Montréal do not use the percentage grading system to convert to the letter grading system. It’s the professor’s responsibilities to convert student’s grade into the letter grading system. They evaluate the students base on their understanding of about the course.
- Université de Laval, Université de Sherbrooke and UQAM’s percentage grading system convert to the letter grading system is different in different programs.
Conclusion
GPA is one of the tools to compare student’s level of understanding. However this is not the only tools. For the employer, they usually looks at which university you come from, how well did you do during the interview, the GPA that you have got, did you fail any course, what kind of activity that you have done for the society, if you have previous job experience, etc. While choosing University, if you want to find a job easily after graduated, you might want to find a University that have COOP program or Internship program. Those programs will let you work in company that is in your domain. If you want to apply to master, schools mostly look at if you have recommendations from professor, meaning if you are going to work for any professor to do research.
Things to consider:
- Chose a good University (base on the program that you want to study)
- Do well in that University
- Try to do more activities outside of school
- If you want to find job easily, chose a University that can offer you a COOP program or Internship program.
- If you want to do Master degree or Ph. D, you should get a good relationship with professor that you want to work for.
Reference
École Hautes Études Commerciales (HEC)
ens30_8-systemes-notation-table-concordance.pdf
École Polytechique de Montréal
explication_systeme_notation.ppt
Université de Montréal (Département d’informatique et de recherche opérationnelle)
École de Technologie Supérieure (ETS)
Université de Sherbrooke
Université de Laval
Université du Québec à Montréal
University of McGill
gi_grading_and_grade_point_averages
University of Concordia
CREPUQ